Floating Bulkhead Saves Dam Operators Time, Money
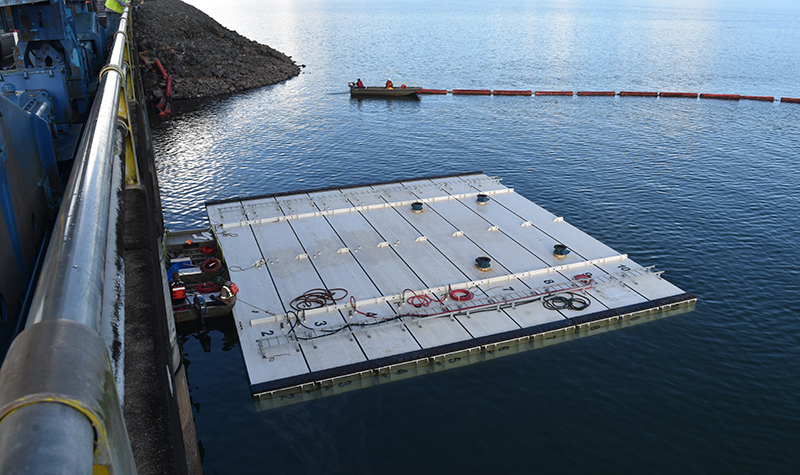

When a dam’s spillway gate needs maintenance or repairs, operators need an efficient way to dewater the structure. Without existing means to dewater a spillway bay, owners may need to dewater the impoundment or fabricate expensive bulkhead systems.
What Is a Cost-Effective Way to Dewater a Dam?
The floating bulkhead allows owners to dewater gates quickly and economically. It can be installed in as little as a day and moved efficiently from bay to bay.
This dewatering system significantly reduces the owner’s costs, provides a safe work environment, and efficiently uses resources. This bulkhead system has been particularly valuable in dewatering tainter gates for rehabilitation and testing.
What Is a Floating Bulkhead?
The floating bulkhead consists of individual floating chambers, or caissons, that are pinned together. Each caisson consists of compartments that are used for flotation of the bulkhead.
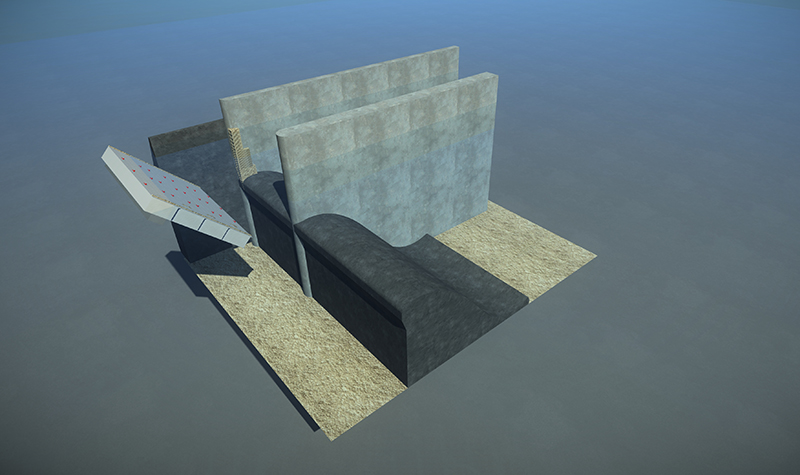
- The floating bulkhead consists of individual floating watertight caissons.
- Filling the lower caissons with water results in rotation and submergence.
- The submerged bulkhead assembly is then pushed up against the spillway to be dewatered.
How Is it Submerged?
As individual caissons and as a completed assembly, a floating bulkhead is buoyant on the reservoir. By flooding and filling the lower caissons with water, the bulkhead rotates vertically and can be pushed into position up against the pier noses.
How Is It Removed?
The floating bulkhead is removed by pumping air into the chambers and evacuating the water; the bulkhead becomes buoyant and floats back up to the surface. The bulkhead can then either be moved to the next spillway bay for testing/repairs or disassembled and removed from the reservoir.
Why Choose a Floating Bulkhead?
- Because the completed bulkhead assembly is buoyant, only a small percentage of the bulkhead’s actual weight rests on the intake or spillway.
- It is easier to transport than conventional bulkheads. The individual caissons can be loaded onto a flatbed truck for site-to-site transport. Once at a site, the segments can be launched in shallow water, connected while floating, and moved by a small boat to the intake or spillway.
- It reduces owner costs. Use of a floating bulkhead significantly reduces owner costs when compared to conventional bulkheads.
- It simplifies the installation and removal process. Because these bulkheads are easy to maneuver and simple to set up, they can be assembled and removed in as little as one day and moved to the next bay for deployment.
The floating bulkhead was developed in 1987 by Xcel Energy and Ayres engineers. Since its initial development, the innovative system has been used at projects across the nation to safely, efficiently, and cost-effectively dewater spillway gates and powerhouse intakes.

Post a comment: